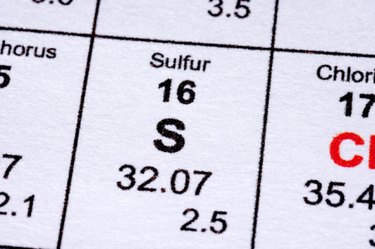
Sulfur is a chemical element that has persisted since prehistoric times. It is pale yellow and non-metallic, with a melting point of 112.8 degrees C and a boiling point of 444.6 degrees C. Sulfur has a variety of uses that humans depend on; for example, it's one of the components of gunpowder and other explosives as well as cement. It also has a range of common household uses.
Fertilizer
Video of the Day
Sulfur is a common component of most fertilizers. When placed on the plant's soil, the sulfur slowly deconstructs with the help of water and oxygen, creating an acid that decreases the soil's pH. The lower a soil's pH, the more iron that becomes naturally accessible to the plant, which helps it grow in a healthy fashion. A range of sulfur fertilizers are available including elemental sulfur, calcium sulfate, thiosulfates and polysulfides.
Video of the Day
Nutrition
One major household use of sulfur is using it to keep your body strong and healthy. According to the website Healthynewage.com, "We need it to produce the amino acid chains necessary to form the protein to rebuild our bodies. The mineral also helps eliminate toxins from the body." Sulfur is present in cabbage, meat, egg yolks, broccoli and onions. An absence or deficiency of sulfur in the body is responsible for weak hair and nails as well as soreness in muscles and joints.
Dermatology
Because sulfur has inherent antifungal and antibacterial properties, people have used it as a topical treatment for acne as well as for other skin issues such as rosacea, scabies, warts, seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff. The precise mechanism of sulfur on these issues is not well understood, according to Aditya K. Gupta and Karyn Nicol, authors of the article "The Use of Sulfur in Dermatology." Scientists just know that it is able to inhibit different types of bacteria and fungus.